How Headings Organize Content on Citadel Websites
Headings create the structure and hierarchy of a webpage. They function like an outline, guiding users, screen readers, search engines and AI tools through content in a logical order.
When headings are used correctly, pages are easier to read, more accessible and easier to maintain. When they’re misused, content becomes confusing—even if it looks “fine” visually.
These standards apply to all Citadel webpages.
Why Heading Structure Matters
Proper heading structure:
- Improves readability and scannability for users
- Allows screen readers to navigate content efficiently
- Helps search engines understand page hierarchy and relevance
- Enables AI tools to accurately summarize and surface content
- Reduces confusion when pages are updated or reorganized
Headings are not a design tool. They are a structural tool.
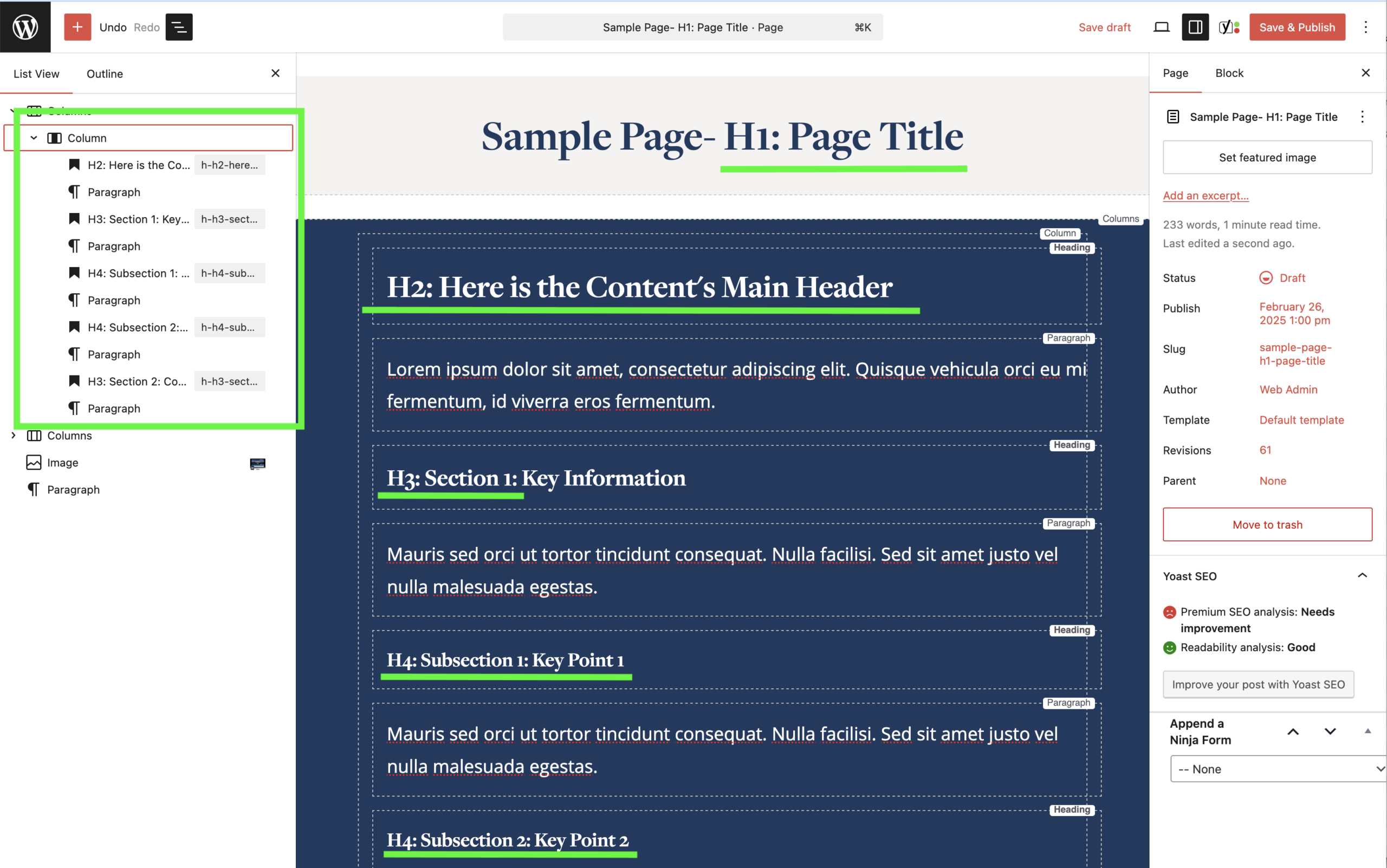
Heading Levels Explained
Each heading level has a specific role. Headings must follow a clear, logical order (H1 → H2 → H3)
Heading 1 (H1)
- Each page must have one H1
- The H1 is the page title
- It defines the main topic of the page
- If your page has more than one H1, the structure is incorrect.
Heading 2 (H2)
- H2s are used for main sections of the page
- Each page should have no more than two H2s
- The first H2 should appear directly below the page title
Important WordPress Note: WordPress often defaults new headings to H2. Editors must manually change heading levels as needed to maintain proper hierarchy.
Heading 3 (H3)
- H3s are used for subsections under an H2
- Limit to three H3s per H2
- H3s should support and expand on the section introduced by the H2
Lower-Level Headings (H4-h6)
- Use sparingly and only when content truly requires additional depth
- Do not use lower-level headings to “style” text
Heading Structure Guidelines
Required Standards:
- Use one H1 per page
- Use H2s for main sections only
- Use H3s for subsections under H2s
- Follow heading levels in order (H1 → H2 → H3)
- Keep headings clear and descriptive
- Use normal capitalization (avoid ALL CAPS)
Never:
- Skip heading levels (do not jump from H1 to H3)
- Choose a heading level based on appearance
- Use headings for decorative or stylistic purposes
- Create multiple H1s on a single page
